PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
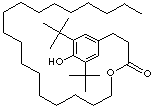
SMILES
CLASSIFICATION
Antioxidant, Stabilizer, Hindered phenolic
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
http://doc.utwente.nl
....It
is important to recognize that different types of inhibitors often
function by different mechanisms, and that a given antioxidant may
react in more than one way. Thus a material that acts as an antioxidant
under one set of conditions may become a pro-oxidant in another
situation. The search for possible synergistic combinations of antioxidants
can be conducted more logically and efficiently if we seek to combine
the effects of different modes of action. Five general modes of
oxidation inhibition are commonly recognized:
1.
Metal deactivators - Organic compounds capable of forming coordination
complexes with metals are known to be useful in inhibiting metal-activated
oxidation. These compounds have multiple coordination sites and
are capable of forming cyclic structures, which “cage” the pro-oxidant
metal ions. EDTA and its various salts are examples of this type
of metal chelating compounds.
2.
Light absorbers – These chemicals protect from photo-oxidation by
absorbing the ultraviolet light energy, which would otherwise initiate
oxidation, either by decomposing a peroxide or by sensitizing the
oxidizable material to oxygen attack. The absorbed energy must be
disposed of by processes, which do not produce activated sites or
free radicals. Fillers which impart opacity to the compound (e.g.
carbon black, zinc oxide) tend to stabilize rubbers against UV catalyzed
oxidation.
3.
Peroxide decomposers – These function by reacting with the initiating
peroxides to form nonradical products. Presumably mercaptans, thiophenols,
and other organic sulfur compounds function in this way.19 It has
been suggested that zinc dialkyldithiocarbamates function as peroxide
decomposers, thus giving rubber compounds good initial oxidative
stability.
4.
Free radical chain stoppers – These chemicals interact with chain
propagating RO2• radicals to form inactive products.
5.
Inhibitor regenerators - These react with intermediates or products
formed in the chain-stopping reaction so as to regenerate the original
inhibitor or form another product capable of functioning as an antioxidant.
Termination
of propagating radicals during the oxidative chain reaction is believed
to be the dominant mechanism by which amine and phenolic antioxidants.......
http://www.thefreelibrary.com/
.....CIBA SPECIALTY CHEMICALS
Irganox high-molecular-weight hindered phenolics provide long-term
oxidative and thermal stability. Irganox 1010 and 1076 have good compatibility
with polyolefins and styrenics and are FDA-regulated. Irganox MD-1024 is a metal
deactivator and all-purpose antioxidant. Irganox 1035, 1010 and MD-1024 are for
wire and cable.
Irganox B-225 and B-215 low-volatility, heat- and
hydrolysis-resistant additive blends reportedly offer excellent processing and
long-term stability in polyolefins.
New FS systems provide polyethylene
fibers and thin-section materials with reportedly exceptional resistance to gas
fade, excellent initial color, and a combination of long-term thermal and uv
stability, in a phenolic-free stabilizer package. FS 812, a new combination of
hindered amine stabilizer, uv absorber and hydroxyl amino processing stabilizer,
offers gloss and color retention for molded-in color applications.
Irganox HP products are synergistic combinations of phenolic
antioxidants, phosphites, and a new lactone processing stabilizer.
The combination results in improved melt flow control, allows for higher
temperature processing, and can result in improved overall processing, heat, and
long-term stability of the polymer.
New Irganox XP processing
stabilizers are combinations of the new lactone processing stabilizer,
high-performance phosphites and phenolic antioxidant. Irganox XP combines
superior compatibility and solubility with outstanding processing stability and
color control.
Irganox E, a vitamin E antioxidant for use in food and
medical packaging offers superior melt flow and color control, low migration,
and superior extraction resistance......
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
97.0% min
SET POINT
VOLATILE MATTER
0.5% max (at 100 C for 2 hrs)
0.1 max (mg KOH/kg)
ASH CONTENT
0.1% max
Not regulated